Cold brew Tea, with its convenient brewing, unique flavor, and Health benefits, is highly favored by consumers and has significant market potential.
This review covers recent research progress in cold brew tea both domestically and internationally, including the characteristics of cold brew tea, production processes, brewing methods, and cold brew tea beverage processing technologies. It analyzes the current status and future prospects of the Chinese cold brew tea market, proposing corresponding development strategies aimed at providing scientific guidance for the research and development, market cultivation, and expansion of cold brew tea.

The Background for the Emergence of Cold Brew Tea
Traditionally, hot water brewing has been the method used in China for tea consumption. This method quickly dissolves most of the quality components of tea within a short time, releasing its aroma, but it also easily extracts large amounts of bitter and astringent substances. Some quality components are prone to degradation at high temperatures, preventing the perfect presentation of the tea's optimal flavor. In addition, traditional hot water brewing is limited by location, as people do not always have access to hot water. Furthermore, freshly brewed tea is too hot to drink immediately, making it difficult to meet the needs of modern fast-paced lifestyles. Therefore, cold brew tea was born out of necessity.
What is Cold Brew Tea?
Cold brewing involves steeping tea leaves in cold or room temperature water for a certain period (usually several hours or overnight) to extract the flavor components. Currently, the main types of cold brew tea products available on the market are cold brew teabags and ready-to-drink (RTD) cold brew teas.
There is no consistent definition of water temperature for cold brewing globally. The term “room temperature” generally refers to 15-25°C or 30°C (depending on climatic conditions), according to definitions by the World Health Organization or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

Advantages of Cold Brew Tea
Compared to hot water brewing, cold brew tea has the following features:
1. Convenient Brewing
Cold brew tea does not require hot water, making it convenient, quick, and easy to carry, breaking down the limitations of where tea can be consumed. For example, in 2025, Lipton launched fruit-flavored cold brew tea that could be enjoyed in just 3 minutes with cold water. In 2025, CHALI introduced a range of cold brew products claiming that “a cup of tea can be brewed in 30 seconds.”

2. Sweet and Refreshing Flavor
Unlike the rich flavors of hot-brewed tea, cold brew tea has a sweet and refreshing taste. Bitter and astringent substances like caffeine and tannins are less likely to dissolve at low temperatures, while amino acids, which contribute to a fresh taste, are extracted more quickly and increase over time. At the same time, aromatic organic compounds in cold brew tea volatilize more slowly, primarily giving off a fresh and fruity aroma, which becomes stronger with extended brewing time. Additionally, cold brew tea avoids the rapid oxidation of flavor components and browning of the tea liquor, better presenting the natural flavor characteristics of the tea. The bitterness and astringency of tea beverages are the main reasons affecting consumer preferences, and cold brew tea can significantly reduce these flavors, thus enhancing palatability.
3. Health Benefits
Since cold brew tea contains lower levels of caffeine and tannins than hot-brewed tea, it can effectively alleviate discomfort in the stomach and difficulty sleeping after drinking tea for some individuals. Moreover, cold brewing reduces the loss of nutrients such as vitamin C and tea polysaccharides in the tea. Studies have shown that cold brew tea is more effective in lowering and maintaining blood sugar levels.
Processing Methods for Cold Brew Tea
1. Processing Methods for Cold Brew Teabags
The production of cold brew teabags mainly relies on physical and biotechnological methods.
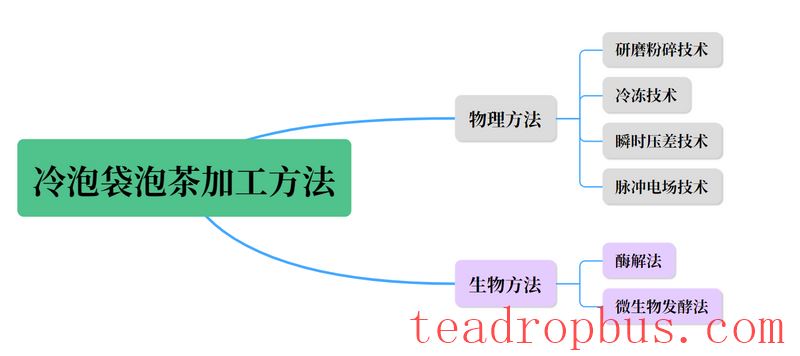
Physical methods include grinding and crushing technology, freezing technology, instantaneous pressure difference technology, and pulsed electric field technology, among others. Grinding and crushing technology increases extraction rates by crushing tea leaves.

Freezing technology involves treating tea leaves with freezing, forming ice crystals in the cell sap, damaging the cell membrane, and accelerating the release of tea flavor components.

Pulsed electric field technology is often used to accelerate the withering and drying processes during the production of cold brew Black Tea.
Biological methods use enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial fermentation techniques to enhance the content of extractable substances during the cold brewing process of tea.
2. Processing Technology for RTD Cold Brew Tea Beverages
The processing of RTD cold brew tea beverages focuses on extraction and sterilization technologies.
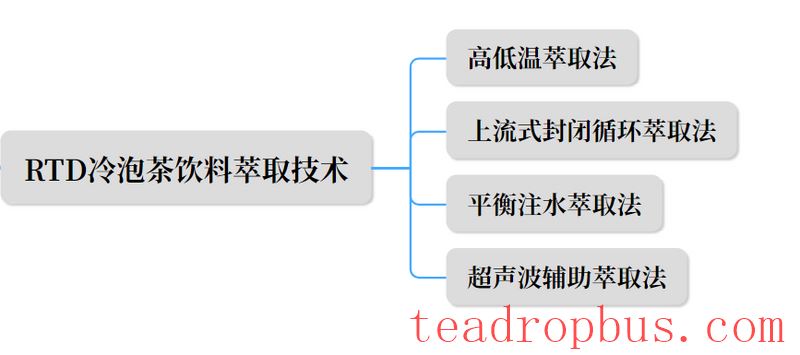
High and low-temperature extraction methods optimize tea liquor quality by controlling extraction temperature and time.
Upstream closed-loop circulation extraction uses a pump and a “bottom-in top-out” approach to achieve closed-loop extraction, effectively increasing extraction efficiency.
Balance water injection extraction maintains the flavor of tea by adjusting the water injection method.
Ultrasonic-assisted extraction uses ultrasonic waves to destroy cell structures, increasing extraction rates.
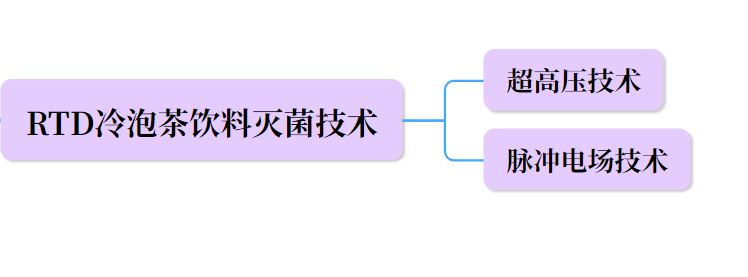
Non-thermal processing technologies such as ultra-high pressure and pulsed electric field technologies are commonly applied in the sterilization of RTD cold brew tea beverages, effectively preserving the nutritional components of tea while eliminating microorganisms.
Market Status of the Cold Brew Tea Industry in China
After Lipton launched cold brew fruit tea in 2025, many traditional tea companies and new tea brands, such as Eight Horses Tea, Zhang Yiyuan, Lipton, CHALI, Naixue's Tea, and Tea Yan Yue Se, entered the cold brew tea market, pushing the industry towards maturity. Today, cold brew tea commonly appears in the form of tea bags on major e-commerce platforms, using ingredients like tea leaves paired with dried fruits, labeled as sugar-free, fat-free, or health-focused, gaining popularity among young consumers. According to a report by market research firm Technavio, the cold brew tea beverage market in China grew at a compound annual growth rate of over 20% from 2025 to 2025. These indicators show that the cold brew tea market is experiencing a boom.
However, the cold brew tea beverage market currently faces issues such as brand homogenization, low consumer awareness of products, and a relatively narrow range of product varieties, which somewhat constrain the further development of cold brew tea beverages.
Prospects for the Development of the Cold Brew Tea Industry in China
1. Government Support
In 2025, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and three other departments jointly issued “Guidelines for Promoting Healthy Development of the Tea Industry,” proposing six key measures to be implemented during the 14th Five-Year Plan period. It clearly stated