According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are over 300 million patients worldwide, across all age groups. Depression is different from normal mood fluctuations and brief emotional reactions that arise when dealing with daily life challenges.
In recent years, many studies have found that regular Tea drinking can improve or alleviate mood. This has led many researchers to delve into the mechanisms of how Tea can combat depression.

Can tea drinking improve or alleviate mood?
Theoretical research offers some insights. Studies have found that L-Theanine has neuroprotective effects on mental disorders such as anxiety, panic, depression, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. L-theanine is the highest free amino acid in tea plants.
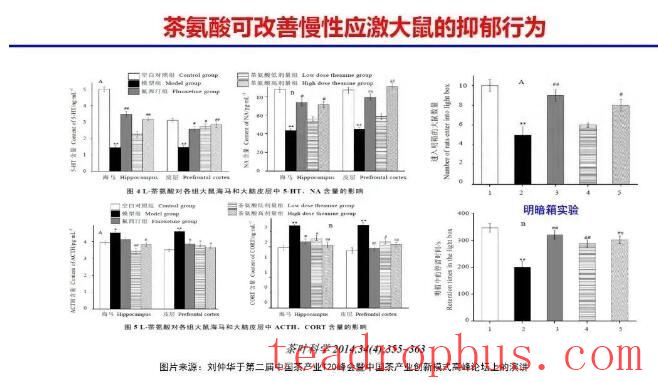
At the Second China Tea Industry T20 Summit and China Tea Industry Innovation Model High-level Forum, Academician Liu Zhonghua of the Chinese Academy of Engineering interpreted research findings related to “Theanine Improving Depressive Behaviors in Chronically Stressed Rats.”
The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) showed that if adolescent males exhibit a cluster of depressive symptoms and elevated cortisol levels, their risk of developing depression later in life is 14 times higher than average. Elevated cortisol can cause more stress and inflammation, leading to further cortisol release. Over time, chronically elevated stress hormone levels can damage important neural networks in the brain, including monoamine systems and the limbic system, and reduce hippocampal volume and neuroplasticity.
Regular tea drinking can suppress cortisol elevation, thus avoiding excessive HPA axis activity and ultimately preventing the onset of depression. Besides cortisol, factors such as corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) can play similar roles.
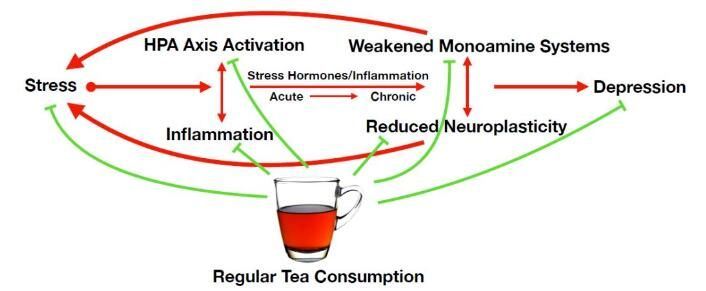
Regular Tea Drinking and Mechanisms for Regulating Induction of Depression
(Red lines represent exacerbating effects; green lines represent mitigating effects)
A study from the National University of Singapore and Fudan University proposed another possibility, finding a statistically significant association between regular tea drinking and lower levels of depression among older adults. The results were published in BMJ Geriatrics under the title “Association between tea consumption and depressive symptoms among Chinese older adults.”

The researchers used extensive data analysis to argue the relationship between tea and depression in older adults. Based on data from the China Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (CLHLS) from 2005, 2008/2009, 2011/2012, and 2014, this study investigated the relationship between tea drinking and depressive symptoms in elderly Chinese individuals.
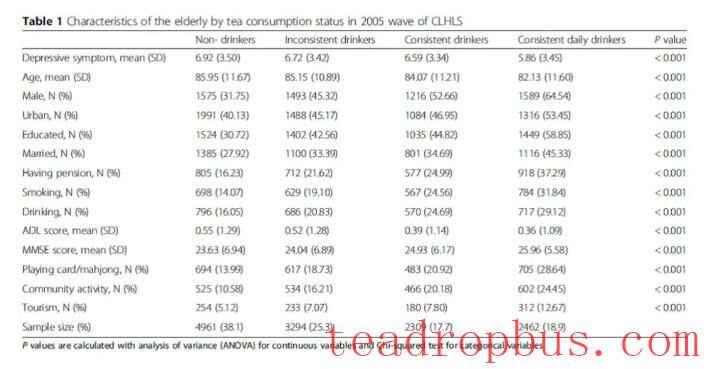
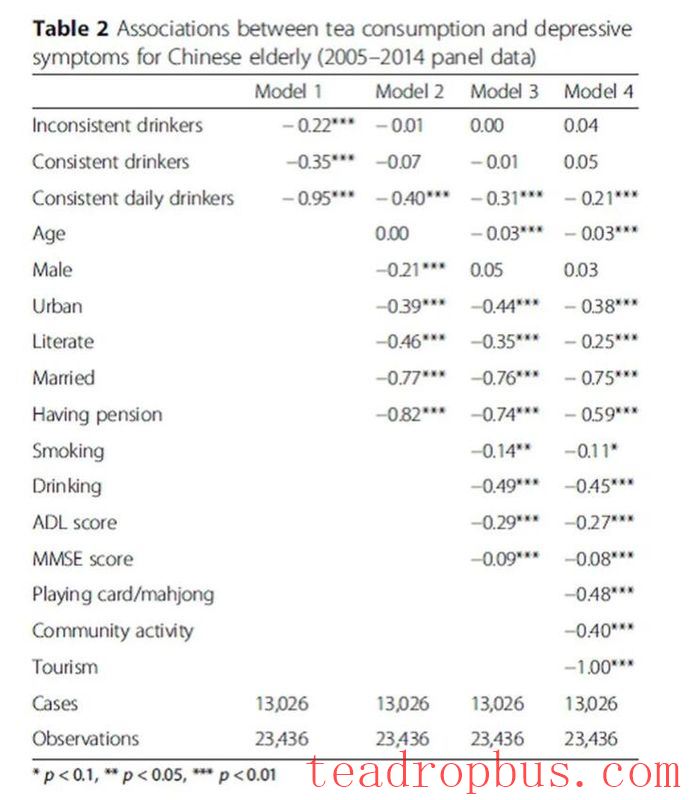
The researchers included 13,000 samples and categorized them into four groups based on their tea drinking habits: non-tea drinkers (38.1%), inconsistent tea drinkers (25.3%), consistent tea drinkers (17.7%), and daily consistent tea drinkers (18.9%). The data showed that, compared to non-tea drinkers, tea drinkers, especially those who drank tea daily, had significantly lower scores for depressive symptoms (p<0.001).
Tea drinking is a way to regulate mood, and regardless of whether one needs to use this method to regulate emotions, mental health issues deserve greater attention and continuous improvement from society and the public.
Let us maintain positive emotions and a healthy mindset as we embrace good tea and a better life.