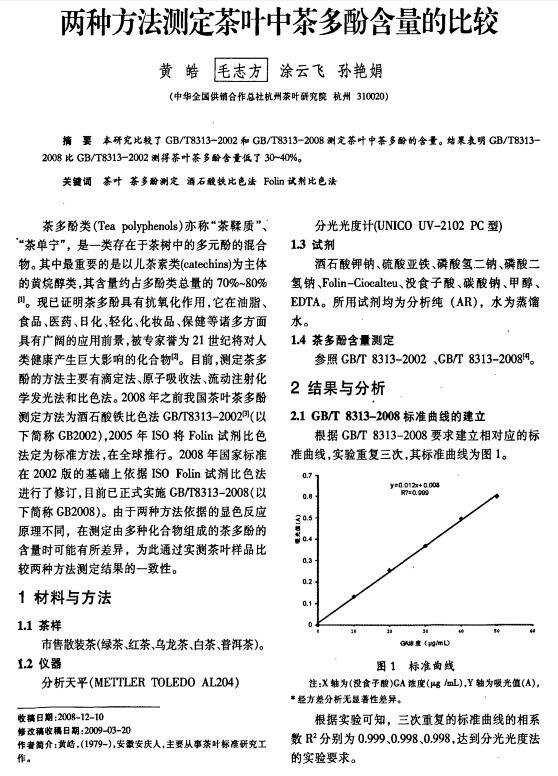
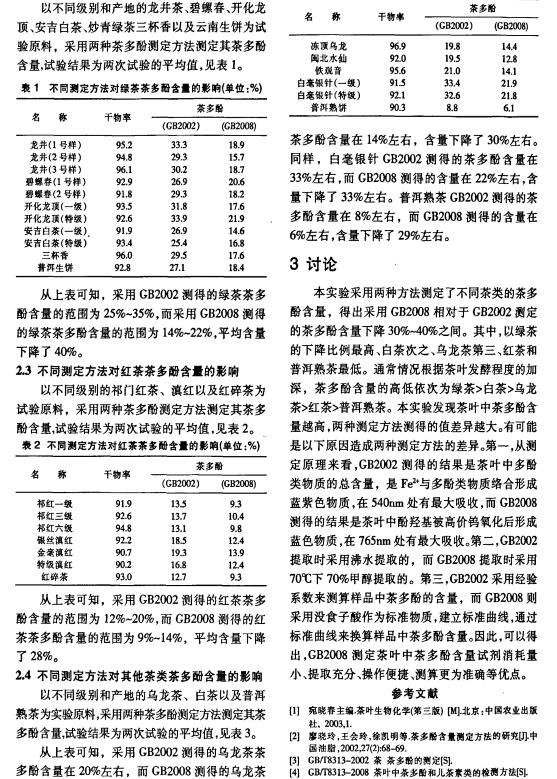
Tea polyphenols (Tea Polyphenols) are a general term for polyphenolic compounds in tea, including flavanols, anthocyanins, flavonoids, flavonols, and phenolic acids. Among these, flavanol compounds (catechins) are the most important, accounting for about 70% of the total tea polyphenols. Tea polyphenols, also known as tea tannins or tea tannin, are one of the main components that form the color, aroma, and taste of tea, as well as one of the key functional ingredients with health benefits. Tea polyphenols appear as a light yellow or light green powder at room temperature, easily soluble in warm water (40°C–80°C) and water-containing ethanol. They exhibit strong stability, remaining stable for 1.5 hours in environments with a pH of 4–8 and temperatures around 250°C, but decompose easily in the presence of ferric ions.